Basic Drawing with Python Turtle Graphics
Basic Drawing with Turtle Graphics:
In this "Basic Drawing with Turtle Graphics" project, the user interacts with the Turtle graphics module by providing commands to draw shapes and patterns. The program outputs a visual representation of the drawing created using Turtle graphics based on the user's input.
Input values:
User interacts with the Turtle graphics module by providing commands to draw shapes and patterns.
Output value:
Visual representation of the drawing created using Turtle graphics.
Example:
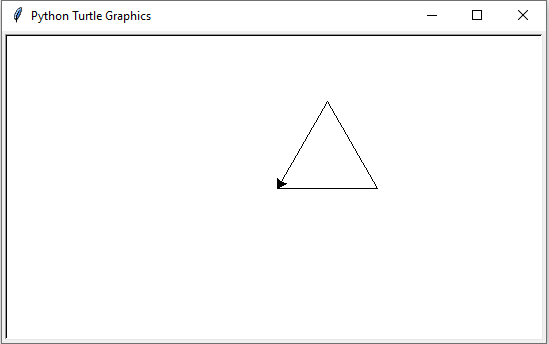
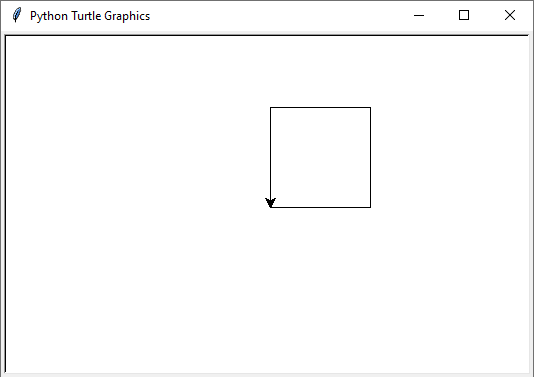
Input values: 1. Move the turtle forward by 100 units 2. Turn the turtle left by 90 degrees 3. Move the turtle forward by 100 units 4. Turn the turtle left by 90 degrees 5. Move the turtle forward by 100 units 6. Turn the turtle left by 90 degrees 7. Move the turtle forward by 100 units Output value: Visual representation displays a square drawn by the Turtle graphics module. Input values: 1. Move the turtle forward by 100 units 2. Turn the turtle left by 120 degrees 3. Move the turtle forward by 100 units 4. Turn the turtle left by 120 degrees 5. Move the turtle forward by 100 units Output value: Visual representation displays an equilateral triangle drawn by the Turtle graphics module.
Solution 1: Basic Drawing using user Commands
This solution uses the "turtle" module to draw shapes based on user input commands. The program accepts commands to move the turtle and change its direction to create various shapes.
Code:
import turtle # Import the turtle module
# Function to process user commands and draw shapes
def draw_shape(commands):
"""Draws a shape based on user-provided commands."""
# Create a turtle screen and turtle object
screen = turtle.Screen()
my_turtle = turtle.Turtle()
# Process each command
for command in commands:
# Move the turtle forward
if command[0] == "move":
my_turtle.forward(command[1])
# Turn the turtle left
elif command[0] == "turn_left":
my_turtle.left(command[1])
# Turn the turtle right
elif command[0] == "turn_right":
my_turtle.right(command[1])
# End the drawing
turtle.done()
# Example usage
# Commands to draw a square
commands_square = [
("move", 100),
("turn_left", 90),
("move", 100),
("turn_left", 90),
("move", 100),
("turn_left", 90),
("move", 100)
]
# Commands to draw a triangle
commands_triangle = [
("move", 100),
("turn_left", 120),
("move", 100),
("turn_left", 120),
("move", 100)
]
# Draw the shapes
#draw_shape(commands_square) # Draw a square
draw_shape(commands_triangle) # Draw a triangle
Output:
Explanation:
- Imports the turtle module to enable drawing capabilities.
- Function draw_shape(commands):
- Creates a turtle screen and object.
- Iterates through user-provided commands to move the turtle forward or turn it left or right.
- Draws the shape based on these commands.
- Example Usage:
- Commands to draw a square: Moves forward and turns left by 90 degrees four times to draw a square.
- Commands to draw a triangle: Moves forward and turns left by 120 degrees three times to draw an equilateral triangle.
Solution 2: Interactive Drawing with Turtle Commands
This solution provides an interactive way for the user to input commands directly in the console to control the turtle and draw shapes.
Code:
import turtle # Import the turtle module
# Function to draw shapes interactively
def interactive_draw():
"""Allows the user to interactively draw shapes using turtle graphics."""
# Create a turtle screen and turtle object
screen = turtle.Screen()
my_turtle = turtle.Turtle()
# Provide instructions to the user
print("Interactive Drawing with Turtle Graphics")
print("Commands: 'move <distance>', 'left <angle>', 'right <angle>', 'exit'")
# Infinite loop to continuously accept user commands
while True:
# Get user input
command = input("Enter command: ").strip().lower()
# Exit the loop if the user types 'exit'
if command == "exit":
print("Exiting drawing.")
break
# Split the command into parts
parts = command.split()
# Validate the command length
if len(parts) != 2:
print("Invalid command format. Use 'move <distance>', 'left <angle>', or 'right <angle>'.")
continue
action, value = parts[0], parts[1]
# Execute the user command
try:
if action == "move":
my_turtle.forward(float(value)) # Move the turtle forward
elif action == "left":
my_turtle.left(float(value)) # Turn the turtle left
elif action == "right":
my_turtle.right(float(value)) # Turn the turtle right
else:
print("Unknown command. Use 'move', 'left', or 'right'.")
except ValueError:
print("Invalid value. Please enter a number.")
# End the drawing
turtle.done()
# Start the interactive drawing
interactive_draw()
Output:
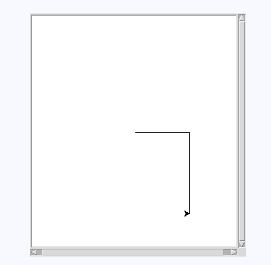
Commands: Interactive Drawing with Turtle Graphics Commands: 'move <distance>', 'left <angle>', 'right <angle>', 'exit' Enter command: move 100 Enter command: right 90 Enter command: move 150 Enter command: left 90 Enter command: exit Exiting drawing.
Explanation:
- Imports the turtle module for drawing.
- Function interactive_draw():
- Creates a turtle screen and object.
- Prints instructions for the user on how to enter commands.
- Accepts user input continuously in a loop to move the turtle (move), turn left (left), or turn right (right).
- Ends drawing when the user types exit.
- User Commands:
- move <distance>: Moves the turtle forward by the specified distance.
- left <angle>: Turns the turtle left by the specified angle.
- right <angle>: Turns the turtle right by the specified angle.
- Summary:
- Solution 1: Automates drawing based on predefined commands.
- Solution 2: Provides an interactive approach, allowing users to manually enter commands for drawing shapes.
Go to: