Python Exercise: N x N square consisting only of the integer N
NxN Square of Integer
Write a Python program that takes a positive integer and creates an N x N square filled with the integer N. Display the N x N square.
Sample Data:
(2) -> [[2, 2], [2, 2]]
(5) -> [[5, 5, 5, 5, 5], [5, 5, 5, 5, 5], [5, 5, 5, 5, 5], [5, 5, 5, 5, 5], [5, 5, 5, 5, 5]]
(-6) -> []
Sample Solution-1:
Python Code:
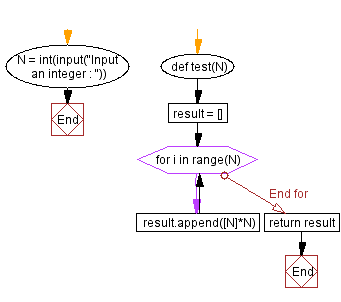
# Function to create a 2D list filled with the value N.
def test(N):
# Initialize an empty list to store the rows.
result = []
# Iterate N times to create N rows.
for i in range(N):
# Append a row with N elements, each having the value N.
result.append([N] * N)
# Return the resulting 2D list.
return result
# Take user input for the value of N.
N = int(input("Input an integer: "))
# Call the test function with the user-input value of N and print the result.
print(test(N))
Sample Output:
Input an integer : 4 [[4, 4, 4, 4], [4, 4, 4, 4], [4, 4, 4, 4], [4, 4, 4, 4]] Input an integer : -4 []
Explanation:
Here is a breakdown of the above Python code:
- Function definition:
- def test(N):: Defines a function named "test()" that takes an integer 'N' as input.
- Initializing an empty list:
- result = []: Initializes an empty list named 'result' to store the rows of the 2D list.
- Loop to create rows:
- for i in range(N):: Iterates 'N' times to create 'N' rows.
- Appending rows:
- result.append([N] * N): Appends a row to the 'result' list. Each row is a list with N elements, and each element has the value 'N'.
- Return result:
- return result: Returns the resulting 2D list.
- User input:
- N = int(input("Input an integer: ")): Takes user input for the value of 'N'.
- Function Call and Print:
- print(test(N)): Calls the "test()" function with the user-input value of 'N' and prints the resulting 2D list.
Flowchart:
Sample Solution-2:
Python Code:
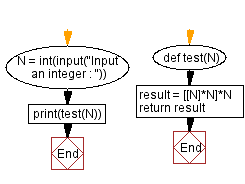
# Function to create a 2D list filled with the value N.
def test(N):
# Create a 2D list with N rows, where each row is a list with N elements, each having the value N.
result = [[N] * N] * N
# Return the resulting 2D list.
return result
# Take user input for the value of N.
N = int(input("Input an integer: "))
# Call the test function with the user-input value of N and print the result.
print(test(N))
Sample Output:
Input an integer : 4 [[4, 4, 4, 4], [4, 4, 4, 4], [4, 4, 4, 4], [4, 4, 4, 4]]
Explanation:
Here is a breakdown of the above Python code:
- Function definition:
- def test(N):: Defines a function named "test()" that takes an integer 'N' as input.
- Creating a 2D List:
- result = [[N] N] N: Creates a 2D list with 'N' rows. Each row is a list with 'N' elements, and each element has the value 'N'.
- Note: This method of creating a 2D list using [...]*N can have unexpected behavior due to the way lists are referenced in Python. It creates references to the same inner list, leading to issues if you modify one row.
- Return result:
- return result: Returns the resulting 2D list.
- User input:
- N = int(input("Input an integer: ")): Takes user input for the value of 'N'.
- Function call and print:
- print(test(N)): Calls the "test()" function with the user-input value of 'N' and prints the resulting 2D list.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Python program to create an N x N matrix filled with the integer N, handling edge cases for non-positive integers.
- Write a Python program to generate a square matrix of size N where each element is the number N using list comprehension.
- Write a Python program to construct and display an N by N grid populated entirely with the integer N.
- Write a Python program to produce an N x N list of lists with all entries equal to N, returning an empty list for negative inputs.
Go to:
Previous: Check the numbers that are higher than the previous
Next: Iterated Cube Root.
Python Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
