Python: Accept an even number from the user and create a combinations that express the given number as a sum of two prime numbers
Goldbach Partition Counter
Write a Python program which accepts an even number (>=4, Goldbach number) from the user and creates combinations which express the given number as a sum of two prime numbers. Print the number of combinations.
Goldbach number: A Goldbach number is a positive even integer that can be expressed as the sum of two odd primes.[4] Since four is the only even number greater than two that requires the even prime 2 in order to be written as the sum of two primes, another form of the statement of Goldbach's conjecture is that all even integers greater than 4 are Goldbach numbers.
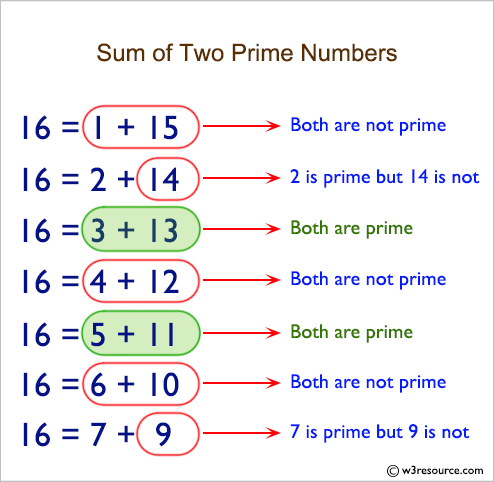
The expression of a given even number as a sum of two primes is called a Goldbach partition of that number. The following are examples of Goldbach partitions for some even numbers:
6 = 3 + 3
8 = 3 + 5
10 = 3 + 7 = 5 + 5
12 = 7 + 5
...
100 = 3 + 97 = 11 + 89 = 17 + 83 = 29 + 71 = 41 + 59 = 47 + 53
Visual Presentation:
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
# Import necessary modules
import sys
from bisect import bisect_right
from itertools import chain
# Print statement to prompt the user to input an even number (0 to exit)
print("Input an even number (0 to exit):")
# Set the upper bound for prime number computation
ub = 50000
# Initialize a boolean list to track prime numbers using the Sieve of Eratosthenes algorithm
is_prime = [0, 0, 1, 1] + [0]*(ub-3)
is_prime[5::6] = is_prime[7::6] = [1]*int(ub/6)
# Initialize a list to store prime numbers
primes = [2, 3]
append = primes.append
# Sieve of Eratosthenes algorithm to find prime numbers
for n in chain(range(5, ub, 6), range(7, ub, 6)):
if is_prime[n]:
append(n)
is_prime[n*3::n*2] = [0]*((ub-n)//(n*2))
primes.sort()
# Infinite loop to continuously accept user input until 0 is entered
for n in map(int, sys.stdin):
# Check if the entered number is 0, and break the loop if true
if not n:
break
# Check if the number is odd
if n % 2:
# Print statement to display the number of combinations
print("Number of combinations:")
# Print the number of combinations using the count of is_prime[n-2]
print(is_prime[n-2])
else:
# Print statement to display the number of combinations
print("Number of combinations:")
# Print the number of combinations using the count of prime pairs that sum to n
print(len([1 for p in primes[:bisect_right(primes, n/2)] if is_prime[n-p]]))
Sample Output:
Input an even number (0 to exit): 100 Number of combinations: 6
Explanation:
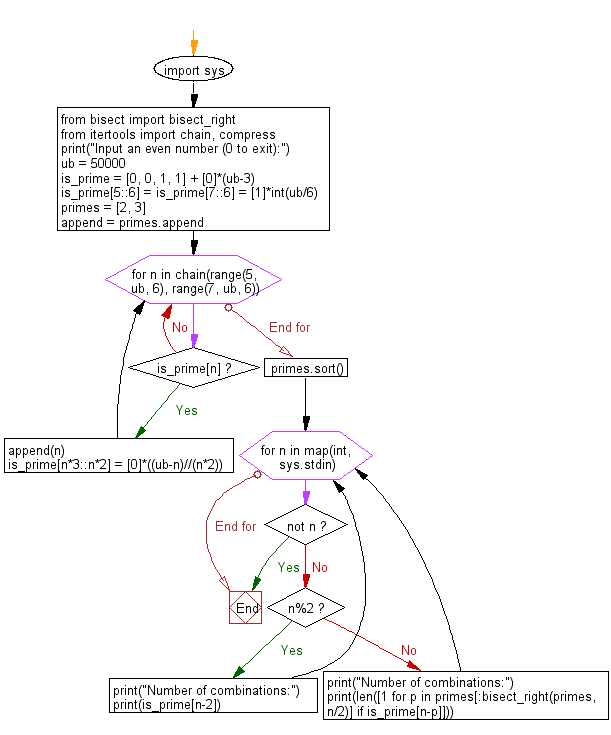
Here is a breakdown of the above Python code:
- First the code initializes the upper bound for prime number computation (ub).
- It initializes a boolean list (is_prime) using the Sieve of Eratosthenes algorithm.
- The code finds prime numbers and stores them in the list (primes).
- It enters an infinite loop to continuously accept user input until 0 is entered.
- Inside the loop, it checks if the entered number is odd and prints the number of combinations using is_prime[n-2].
- If the number is even, it prints the number of combinations using the count of prime pairs that sum to 'n'.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Python program to count all Goldbach partitions of a given even number using an optimized prime sieve.
- Write a Python program to list every unique pair of odd primes that sum to a given even number and count these pairs.
- Write a Python program to verify Goldbach’s conjecture for a range of even numbers and display the number of partitions for each.
- Write a Python program to determine the Goldbach partition with the smallest difference between the two prime numbers.
Go to:
Previous: Write a Python program to compute the sum of first n given prime numbers.
Next: Write a Python program to create maximum number of regions obtained by drawing n given straight lines.
Python Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
