Implementing a Python decorator to measure memory usage of a function
11. Implement a Decorator to Measure Memory Usage of a Function
Write a Python program that implements a decorator to measure the memory usage of a function.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
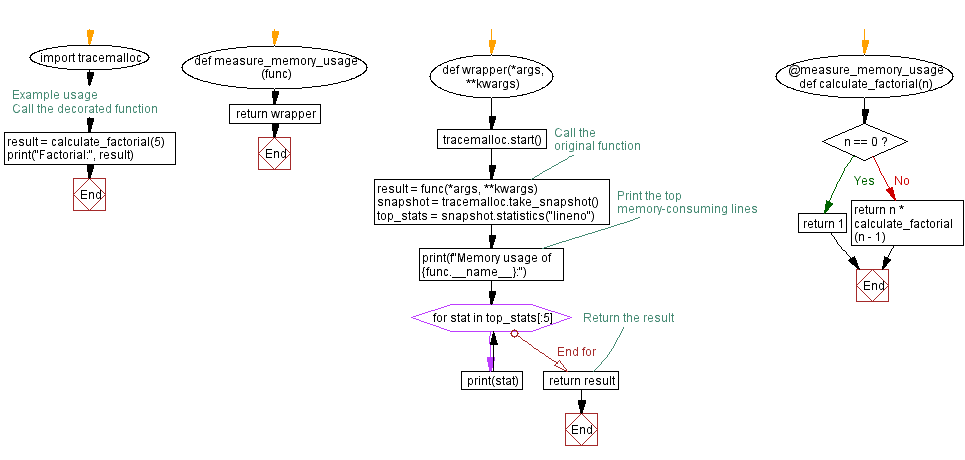
import tracemalloc
def measure_memory_usage(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
tracemalloc.start()
# Call the original function
result = func(*args, **kwargs)
snapshot = tracemalloc.take_snapshot()
top_stats = snapshot.statistics("lineno")
# Print the top memory-consuming lines
print(f"Memory usage of {func.__name__}:")
for stat in top_stats[:5]:
print(stat)
# Return the result
return result
return wrapper
# Example usage
@measure_memory_usage
def calculate_factorial(n):
if n == 0:
return 1
else:
return n * calculate_factorial(n - 1)
# Call the decorated function
result = calculate_factorial(5)
print("Factorial:", result)
Sample Output:
Memory usage of calculate_factorial: /tmp/sessions/aeafebf7cb54338f/main.py:29: size=2128 B, count=9, average=236 B /tmp/sessions/aeafebf7cb54338f/main.py:8: size=1376 B, count=5, average=275 B /tmp/sessions/aeafebf7cb54338f/main.py:10: size=416 B, count=1, average=416 B Memory usage of calculate_factorial: /tmp/sessions/aeafebf7cb54338f/main.py:29: size=2128 B, count=9, average=236 B /tmp/sessions/aeafebf7cb54338f/main.py:8: size=1312 B, count=4, average=328 B /usr/local/lib/python3.10/tracemalloc.py:226: size=880 B, count=3, average=293 B /usr/local/lib/python3.10/tracemalloc.py:173: size=800 B, count=2, average=400 B /usr/local/lib/python3.10/tracemalloc.py:533: size=568 B, count=1, average=568 B Memory usage of calculate_factorial: /tmp/sessions/aeafebf7cb54338f/main.py:29: size=2016 B, count=7, average=288 B /usr/local/lib/python3.10/tracemalloc.py:67: size=1280 B, count=20, average=64 B /usr/local/lib/python3.10/tracemalloc.py:535: size=1240 B, count=3, average=413 B /usr/local/lib/python3.10/tracemalloc.py:193: size=1104 B, count=23, average=48 B /usr/local/lib/python3.10/tracemalloc.py:226: size=880 B, count=3, average=293 B Memory usage of calculate_factorial: /tmp/sessions/aeafebf7cb54338f/main.py:29: size=1904 B, count=5, average=381 B /usr/local/lib/python3.10/tracemalloc.py:558: size=1416 B, count=29, average=49 B /usr/local/lib/python3.10/tracemalloc.py:67: size=1344 B, count=21, average=64 B /usr/local/lib/python3.10/tracemalloc.py:535: size=1240 B, count=3, average=413 B /usr/local/lib/python3.10/tracemalloc.py:226: size=832 B, count=2, average=416 B Memory usage of calculate_factorial: /tmp/sessions/aeafebf7cb54338f/main.py:29: size=1856 B, count=4, average=464 B /usr/local/lib/python3.10/tracemalloc.py:67: size=1408 B, count=22, average=64 B /usr/local/lib/python3.10/tracemalloc.py:535: size=1240 B, count=3, average=413 B /usr/local/lib/python3.10/tracemalloc.py:558: size=1232 B, count=25, average=49 B /usr/local/lib/python3.10/tracemalloc.py:226: size=880 B, count=3, average=293 B Factorial: 24
Explanation:
In the above exercise -
The decorator function "measure_memory_usage()" measures the memory usage of a function using the tracemalloc module. Here's a brief explanation of the code:
- The measure_memory_usage decorator takes a function func as an argument.
- Within the wrapper function, tracemalloc.start() is called to start tracing memory allocations.
- The original function func is called with the provided arguments and the result is stored in the result variable.
- tracemalloc.take_snapshot() is used to take a snapshot of the memory allocation at that point in the code.
- The snapshot is used to retrieve memory statistics using snapshot.statistics("lineno"). This returns a list of statistics sorted by line number.
- The decorator then prints the top memory-consuming lines by iterating over the top_stats list and printing them.
- Finally, the original function result is returned.
In the example,
- The calculate_factorial function is decorated with @measure_memory_usage to measure its memory usage.
- The decorated function is called with an argument of 5 to calculate the factorial.
- The factorial result is printed along with the memory usage statistics obtained from the decorator.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Python decorator that uses the psutil module to record memory usage before and after a function call and prints the difference.
- Write a Python decorator that logs the peak memory usage during the execution of a function.
- Write a Python decorator that returns a tuple containing both the function result and its memory usage measured in bytes.
- Write a Python decorator that uses a memory profiler to monitor and report memory usage for long-running functions.
Go to:
Previous: Implementing a Python decorator for enforcing type checking on function arguments.
Next: Implementing a Python decorator for caching with expiration time in functions.
Python Code Editor :
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
