Implementing a Python decorator for function rate limits
7. Implement a Decorator to Enforce Rate Limits on a Function
Write a Python program that implements a decorator to enforce rate limits on a function.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
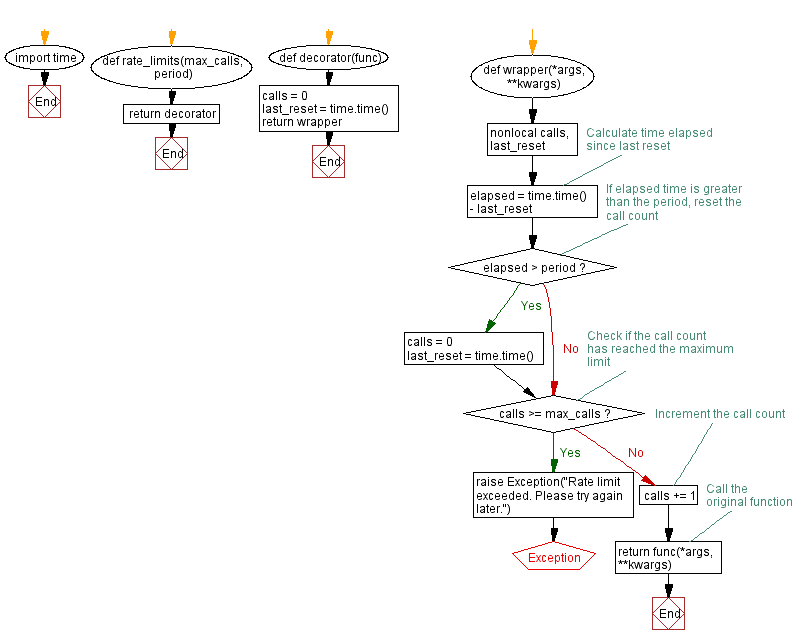
import time
def rate_limits(max_calls, period):
def decorator(func):
calls = 0
last_reset = time.time()
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
nonlocal calls, last_reset
# Calculate time elapsed since last reset
elapsed = time.time() - last_reset
# If elapsed time is greater than the period, reset the call count
if elapsed > period:
calls = 0
last_reset = time.time()
# Check if the call count has reached the maximum limit
if calls >= max_calls:
raise Exception("Rate limit exceeded. Please try again later.")
# Increment the call count
calls += 1
# Call the original function
return func(*args, **kwargs)
return wrapper
return decorator
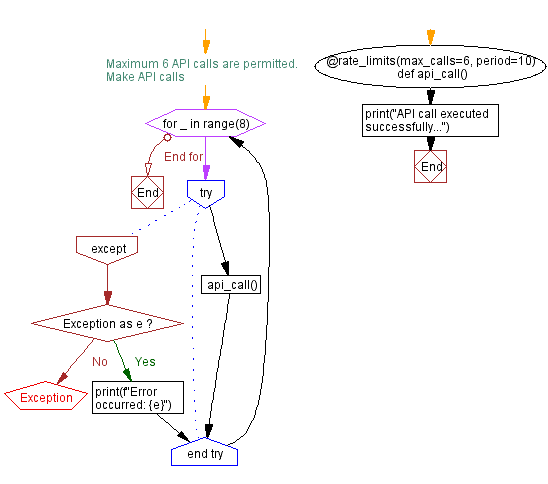
# Maximum 6 API calls are permitted.
@rate_limits(max_calls=6, period=10)
def api_call():
print("API call executed successfully...")
# Make API calls
for _ in range(8):
try:
api_call()
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error occurred: {e}")
Sample Output:
API call executed successfully... API call executed successfully... API call executed successfully... API call executed successfully... API call executed successfully... API call executed successfully... Error occurred: Rate limit exceeded. Please try again later. Error occurred: Rate limit exceeded. Please try again later.
Explanation:
In the above exercise -
- The rate_limits decorator is defined with two parameters: max_calls and period. It limits the number of function calls within a specified time period.
- Inside the decorator, a "calls" counter and a last_reset timestamp are initialized to keep track of the number of calls made and the last time the counter was reset.
- The wrapper function is defined inside the decorator and is responsible for enforcing the rate limit and calling the original function.
- Inside the wrapper function, the elapsed time since the last reset is calculated.
- If the elapsed time is longer than the specified period, the "calls" counter is reset to 0, and the last_reset timestamp is updated to the current time.
- The current call count is checked against the maximum limit specified by max_calls. If the limit is exceeded, an exception is raised.
- If the call count is within the limit, the counter is incremented, and the original function is called.
- Finally, the wrapper function returns the decorator result.
- The api_call function is decorated using @rate_limits(max_calls=6, period=10) syntax, indicating that a maximum of 6 API calls are allowed within a 10-second period.
- In the example code, a loop makes 8 API calls. The first 6 calls execute successfully, but the 7th and 8th calls raise an exception indicating that the rate limit has been exceeded.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Python decorator that limits a function’s call frequency to a maximum number of calls per minute using time stamps.
- Write a Python decorator that implements a sliding window rate limiter, preventing function execution if the rate limit is exceeded.
- Write a Python decorator that raises an exception if a function is called more than a set number of times within a given time interval.
- Write a Python decorator that queues calls to a function and delays execution until the rate limit allows it.
Go to:
Previous: Implementing a Python decorator for function retry.
Next: Implementing a Python decorator for function logging.
Python Code Editor :
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
