Python: Perform a deep flattens a list
Deep Flatten a List
Write a Python program to perform a deep flattening of a list.
- Use recursion.
- Use isinstance() with collections.abc.Iterable to check if an element is iterable.
- If it is iterable, apply deep_flatten() recursively, otherwise return [lst].
Sample Solution:
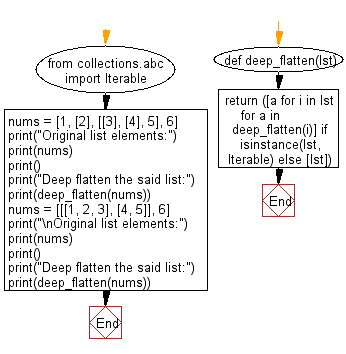
Python Code:
from collections.abc import Iterable
# Define a function to deeply flatten a nested list.
def deep_flatten(lst):
# Check if the input is an iterable (e.g., a list or nested list).
if isinstance(lst, Iterable):
# Use list comprehensions to recursively flatten nested lists.
return [a for i in lst for a in deep_flatten(i)]
else:
# If the input is not an iterable, return a list containing the input element.
return [lst]
# Example 1
nums = [1, [2], [[3], [4], 5], 6]
print("Original list elements:")
print(nums)
print()
print("Deep flatten the said list:")
print(deep_flatten(nums))
# Example 2
nums = [[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5]], 6]
print("\nOriginal list elements:")
print(nums)
print()
print("Deep flatten the said list:")
print(deep_flatten(nums))
Sample Output:
Original list elements: [1, [2], [[3], [4], 5], 6] Deep flatten the said list: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] Original list elements: [[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5]], 6] Deep flatten the said list: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Python program to deeply flatten a list that contains nested lists, tuples, and sets into a single flat list.
- Write a Python program to flatten a nested list structure recursively, handling any depth of nesting.
- Write a Python program to flatten a list with mixed types (e.g., dictionaries, lists) while preserving the order of numeric elements.
- Write a Python program to perform a deep flatten of a list and then sort the resulting flat list in ascending order.
Go to:
Previous: Write a Python program to get the weighted average of two or more numbers.
Next: Write a Python program to get the powerset of a given iterable.
Python Code Editor:
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
