Ordinary differential equations with NumPy and SciPy
8. Solving ODEs with SciPy
Write a Numpy program to create a NumPy array and use SciPy to solve a system of ordinary differential equations (ODEs).
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
# Import necessary libraries
import numpy as np
from scipy.integrate import odeint
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Define the system of ODEs
def model(y, t):
dydt = -2 * y + np.sin(t)
return dydt
# Create a NumPy array for initial conditions
y0 = np.array([1.0])
# Create a time array using NumPy
t = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
# Use SciPy's odeint function to solve the ODEs
solution = odeint(model, y0, t)
# Plot the solution
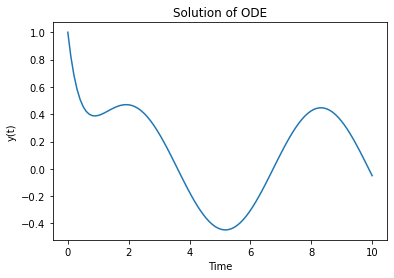
plt.plot(t, solution)
plt.xlabel('Time')
plt.ylabel('y(t)')
plt.title('Solution of ODE')
plt.show()
Output:
Explanation:
- Import necessary libraries:
- Import NumPy for array operations, SciPy's odeint function for solving ODEs, and Matplotlib for plotting.
- Define the system of ODEs:
- Create a function model that represents the ODE dydt=−2y+sin(t)\frac{dy}{dt} = -2y + \sin(t)dtdy=−2y+sin(t).
- Create a NumPy array for initial conditions:
- Initialize the starting value of yyy.
- Create a time array using NumPy:
- Generate an array of time points from 0 to 10.
- Use SciPy's odeint function to solve the ODEs:
- Pass the model, initial condition, and time array to odeint to solve the ODE.
- Finally use Matplotlib to visualize the solution of the ODE over time.
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Numpy program to solve a simple harmonic oscillator ODE using SciPy's odeint and plot the solution.
- Write a Numpy program to solve a system of first-order ODEs modeling predator-prey dynamics using SciPy.
- Write a Numpy program to compare the solutions of an ODE obtained by SciPy's solve_ivp and odeint methods.
- Write a Numpy program to solve an ODE with varying initial conditions and visualize how the solution evolves over time.
Go to:
PREV : Hypothesis Testing with SciPy Stats.
NEXT : Multidimensional Scaling (MDS).
Python-Numpy Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.