NumPy: Change the dimension of an array
Change Array Dimensions
Write a NumPy program to change an array's dimension.
Pictorial Presentation:
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
# Importing the NumPy library with an alias 'np'
import numpy as np
# Creating a NumPy array with 6 elements
x = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
# Printing the shape of the array (6 rows and 0 columns)
print("6 rows and 0 columns")
print(x.shape)
# Creating a 2D array (3x3 matrix)
y = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]])
# Printing the shape and content of the array (3 rows and 3 columns)
print("(3, 3) -> 3 rows and 3 columns ")
print(y)
# Creating a 1D array with 9 elements
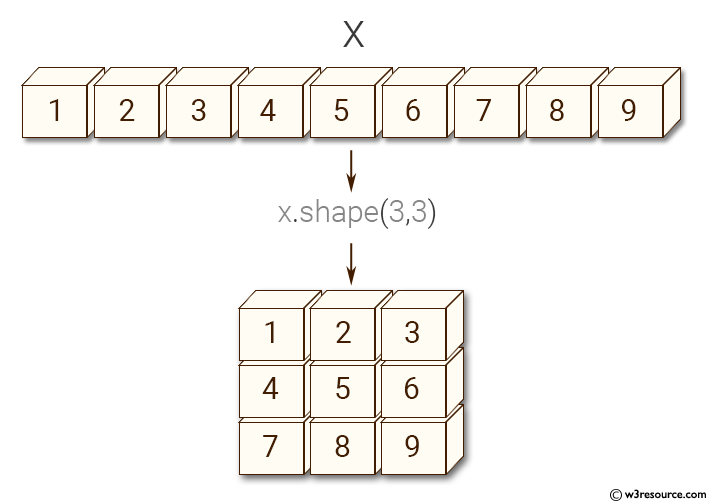
x = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
# Changing the shape of the array to (3, 3) -> 3 rows and 3 columns
x.shape = (3, 3)
# Printing the array after changing its shape
print("Change array shape to (3, 3) -> 3 rows and 3 columns ")
print(x)
Sample Output:
6 rows and 0 columns (6,) (3, 3) -> 3 rows and 3 columns [[1 2 3] [4 5 6] [7 8 9]] Change array shape to (3, 3) -> 3 rows and 3 columns [[1 2 3] [4 5 6] [7 8 9]]
Explanation:
In the above code -
x = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]): The present line creates a one-dimensional NumPy array ‘x’ with elements from 1 to 6.
y = np.array([[1, 2, 3],[4, 5, 6],[7,8,9]]): The present line creates a two-dimensional NumPy array ‘y’ of shape (3, 3) with elements from 1 to 9.
x = np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]): The present line reassigns ‘x’ to a new one-dimensional NumPy array with elements from 1 to 9.
x.shape = (3, 3): The present line reshapes the one-dimensional ‘x’ array into a two-dimensional array of shape (3, 3) by modifying its shape attribute directly.
print(x): Finally print() function prints the reshaped ‘x’ array, which now has the same shape and elements as the ‘y’ array.
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Reshape a 1D array into a 2D array with specified rows and columns and validate the new shape.
- Create a function that reshapes an array and then flattens it back to its original dimensions.
- Handle errors when the desired new shape is incompatible with the original number of elements.
- Compare the use of np.reshape with manual re-indexing to achieve the same dimensional transformation.
Go to:
PREV : Create Zeros and Ones Array
NEXT : Flatten Array
Python-Numpy Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
