Python Object-Oriented Programming: Linked list class with insertion, deletion, and display methods
7. Linked List Data Structure Class
Write a Python program to create a class representing a linked list data structure. Include methods for displaying linked list data, inserting and deleting nodes.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
# Define a class called Node to represent a node in a linked list
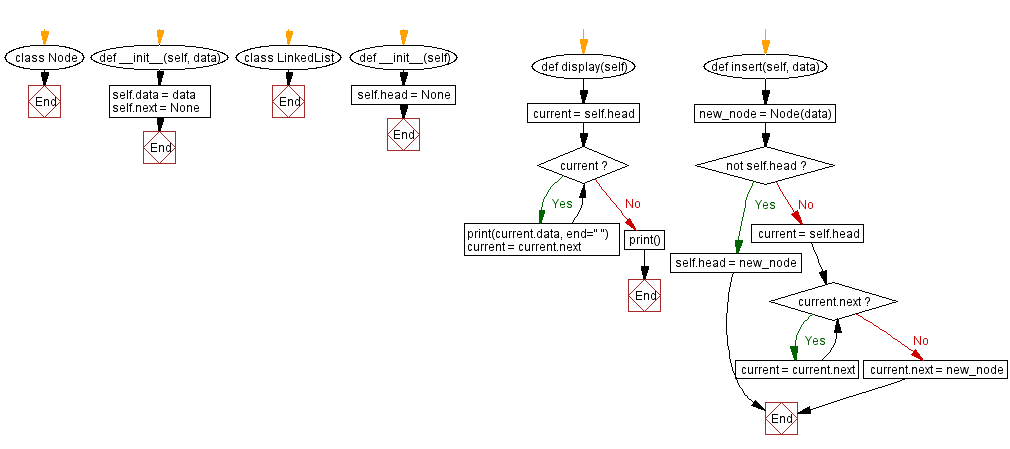
class Node:
# Initialize the Node object with data and set the next pointer to None
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
# Define a class called LinkedList to represent a singly linked list
class LinkedList:
# Initialize the linked list with an empty head node
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Display the elements in the linked list
def display(self):
current = self.head
while current:
print(current.data, end=" ")
current = current.next
print()
# Insert a new node with the given data at the end of the linked list
def insert(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
if not self.head:
self.head = new_node
else:
current = self.head
while current.next:
current = current.next
current.next = new_node
# Delete a node with the given data from the linked list
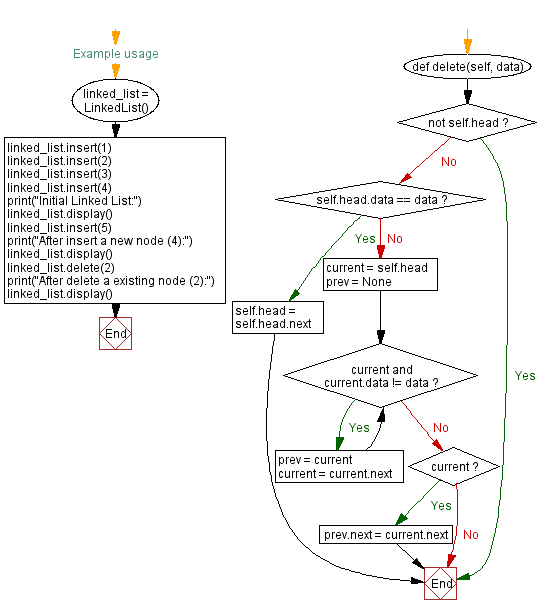
def delete(self, data):
if not self.head:
return
if self.head.data == data:
self.head = self.head.next
return
current = self.head
prev = None
while current and current.data != data:
prev = current
current = current.next
if current:
prev.next = current.next
# Example usage
# Create an instance of the LinkedList class
linked_list = LinkedList()
# Insert elements into the linked list
linked_list.insert(1)
linked_list.insert(2)
linked_list.insert(3)
linked_list.insert(4)
# Display the initial linked list
print("Initial Linked List:")
linked_list.display()
# Insert a new node with data 5 into the linked list
linked_list.insert(5)
print("After inserting a new node (5):")
linked_list.display()
# Delete a node with data 2 from the linked list
linked_list.delete(2)
print("After deleting an existing node (2):")
linked_list.display()
Sample Output:
Initial Linked List: 1 2 3 4 After insert a new node (4): 1 2 3 4 5 After delete a existing node (2): 1 3 4 5
Explanation:
In this above exercise,
- We define a Node class representing a node in the linked list. Each node contains some data and a reference to the next node (or None if it's the last node).
- The LinkedList class represents the linked list itself. It has a head attribute that points to the first node in the list.
- The "display()" method traverses the linked list from the head and prints the data of each node.
- The "insert()" method inserts a new node at the end of the linked list. If the list is empty (head is None), it creates an empty node and sets it as the head.
- The "delete()" method removes the first occurrence of a node with the specified data from the linked list. It handles the case when the node to be deleted is the head separately.
- In the example usage section, we create an instance of the LinkedList class called linked_list. We insert several nodes into the list using the insert method. The initial linked list is then displayed using the display method.
- We demonstrate inserting a new node into the list as well as deleting a node from the list and then display the updated list.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Python class for a singly linked list that includes methods for inserting a node at the beginning and deleting a node by value.
- Write a Python class for a linked list that implements a method to reverse the list in place.
- Write a Python class for a linked list that supports searching for a node by value and returns its index if found.
- Write a Python class for a linked list that prints its elements and also returns its length by iterating through the list.
Go to:
Previous: Stack class with push and pop methods.
Next: Shopping cart class with item management and total calculation.
Python Code Editor:
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
