Python: Find the indices for which the numbers in the list drops
Indices of Drops in List
Write a Python program to find the indices at which the numbers in the list drop.
NOTE: You can detect multiple drops just by checking if nums[i] < nums[i-1].
Input: [0, -1, 3, 8, 5, 9, 8, 14, 2, 4, 3, -10, 10, 17, 41, 22, -4, -4, -15, 0] Output: [1, 4, 6, 8, 10, 11, 15, 16, 18] Input: [6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1] Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] Input: [1, 19, 5, 15, 5, 25, 5] Output: [2, 4, 6]
Sample Solution-1:
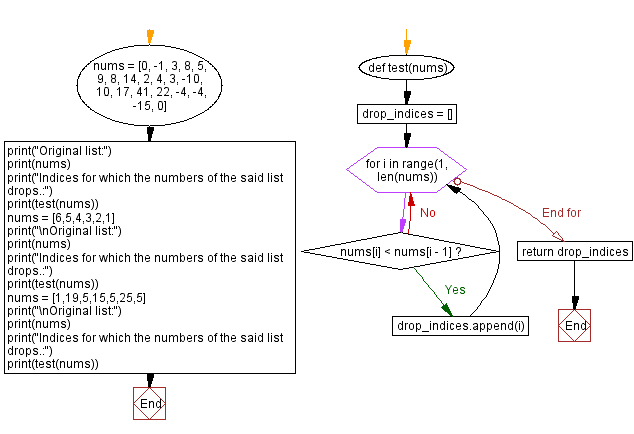
Python Code:
# License: https://bit.ly/3oLErEI
# Define a function named 'test' that takes a list of numbers 'nums' as input
def test(nums):
# Initialize an empty list 'drop_indices' to store indices where numbers drop
drop_indices = []
# Iterate through the list starting from the second element
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
# Check if the current number is less than the previous number
if nums[i] < nums[i - 1]:
# If true, append the index to 'drop_indices'
drop_indices.append(i)
# Return the list of indices where the numbers drop
return drop_indices
# Assign a specific list of numbers 'nums' to the variable
nums = [0, -1, 3, 8, 5, 9, 8, 14, 2, 4, 3, -10, 10, 17, 41, 22, -4, -4, -15, 0]
# Print the original list of numbers 'nums'
print("Original list:")
print(nums)
# Print a message indicating the operation to be performed
print("Indices for which the numbers of the said list drops:")
# Print the result of the test function applied to the 'nums' list
print(test(nums))
# Assign a different list of numbers 'nums' to the variable
nums = [6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
# Print the original list of numbers 'nums'
print("\nOriginal list:")
print(nums)
# Print a message indicating the operation to be performed
print("Indices for which the numbers of the said list drops:")
# Print the result of the test function applied to the updated 'nums' list
print(test(nums))
# Assign another list of numbers 'nums' to the variable
nums = [1, 19, 5, 15, 5, 25, 5]
# Print the original list of numbers 'nums'
print("\nOriginal list:")
print(nums)
# Print a message indicating the operation to be performed
print("Indices for which the numbers of the said list drops:")
# Print the result of the test function applied to the updated 'nums' list
print(test(nums))
Sample Output:
Original list: [0, -1, 3, 8, 5, 9, 8, 14, 2, 4, 3, -10, 10, 17, 41, 22, -4, -4, -15, 0] Indices for which the numbers of the said list drops.: [1, 4, 6, 8, 10, 11, 15, 16, 18] Original list: [6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1] Indices for which the numbers of the said list drops.: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] Original list: [1, 19, 5, 15, 5, 25, 5] Indices for which the numbers of the said list drops.: [2, 4, 6]
Flowchart:
Sample Solution-2:
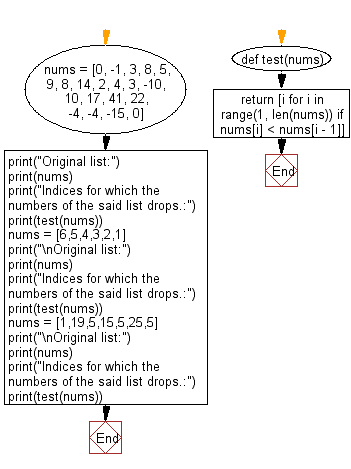
Python Code:
# License: https://bit.ly/3oLErEI
# Define a function named 'test' that takes a list of numbers 'nums' as input
def test(nums):
# List comprehension to create a list of indices where the numbers drop
# Iterate through the list starting from the second element
# Check if the current number is less than the previous number
# If true, include the index in the resulting list
return [i for i in range(1, len(nums)) if nums[i] < nums[i - 1]]
# Assign a specific list of numbers 'nums' to the variable
nums = [0, -1, 3, 8, 5, 9, 8, 14, 2, 4, 3, -10, 10, 17, 41, 22, -4, -4, -15, 0]
# Print the original list of numbers 'nums'
print("Original list:")
print(nums)
# Print a message indicating the operation to be performed
print("Indices for which the numbers of the said list drops:")
# Print the result of the test function applied to the 'nums' list
print(test(nums))
# Assign a different list of numbers 'nums' to the variable
nums = [6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
# Print the original list of numbers 'nums'
print("\nOriginal list:")
print(nums)
# Print a message indicating the operation to be performed
print("Indices for which the numbers of the said list drops:")
# Print the result of the test function applied to the updated 'nums' list
print(test(nums))
# Assign another list of numbers 'nums' to the variable
nums = [1, 19, 5, 15, 5, 25, 5]
# Print the original list of numbers 'nums'
print("\nOriginal list:")
print(nums)
# Print a message indicating the operation to be performed
print("Indices for which the numbers of the said list drops:")
# Print the result of the test function applied to the updated 'nums' list
print(test(nums))
Sample Output:
Original list: [0, -1, 3, 8, 5, 9, 8, 14, 2, 4, 3, -10, 10, 17, 41, 22, -4, -4, -15, 0] Indices for which the numbers of the said list drops.: [1, 4, 6, 8, 10, 11, 15, 16, 18] Original list: [6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1] Indices for which the numbers of the said list drops.: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] Original list: [1, 19, 5, 15, 5, 25, 5] Indices for which the numbers of the said list drops.: [2, 4, 6]
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Python program to identify indices where the current element is less than the previous element in a list.
- Write a Python program to iterate over a list and collect positions where a drop in value occurs using enumerate().
- Write a Python program to compare each element with its predecessor and return all indices of decreases.
- Write a Python program to use a list comprehension to gather indices where a drop in sequence value is detected.
Go to:
Previous: Compute the sum of the ASCII values of the upper-case characters in a given string.
Next: Create a list whose ith element is the maximum of the first i elements of the input list.
Python Code Editor :
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
