Creating a text display application with PyQt
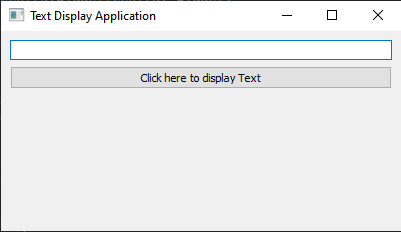
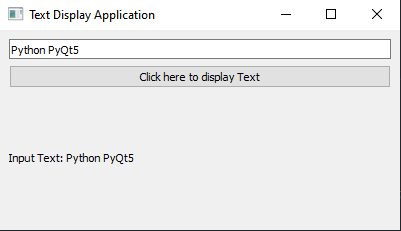
Write a Python program that creates a PyQt application with a QLineEdit widget and a QPushButton. When the button is clicked, it should display the text entered in QLineEdit
Note:
The QLineEdit widget is a one-line text editor.
The QPushButton widget provides a command button.
From doc.qt.io:
QApplication Class: The QApplication class manages the GUI application's control flow and main settings.
QMainWindow Class: The QMainWindow class provides a main application window.
QLabel Class: The QLabel widget provides a text or image display.
QLineEdit Class: A line edit allows the user to enter and edit a single line of plain text with a useful collection of editing functions, including undo and redo, cut and paste, and drag and drop.
QPushButton: The push button, or command button, is perhaps the most commonly used widget in any graphical user interface. Push (click) a button to command the computer to perform some action, or to answer a question. Typical buttons are OK, Apply, Cancel, Close, Yes, No and Help.
QVBoxLayout Class: This class is used to construct vertical box layout objects.
QWidget: The QWidget class is the base class of all user interface objects.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QLabel, QLineEdit, QPushButton, QVBoxLayout, QWidget
class TextDisplayApp(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
# Set the window properties (title and initial size)
self.setWindowTitle("Text Display Application")
self.setGeometry(100, 100, 400, 200) # (x, y, width, height)
# Create a central widget for the main window
central_widget = QWidget()
self.setCentralWidget(central_widget)
# Create widgets (QLineEdit, QPushButton, and QLabel)
self.text_edit = QLineEdit()
self.display_button = QPushButton("Click here to display Text")
self.result_label = QLabel("")
# Create a vertical layout
layout = QVBoxLayout()
# Add widgets to the layout
layout.addWidget(self.text_edit)
layout.addWidget(self.display_button)
layout.addWidget(self.result_label)
# Set the layout for the central widget
central_widget.setLayout(layout)
# Connect the button click event to the display_text function
self.display_button.clicked.connect(self.display_text)
def display_text(self):
# Get the text from the QLineEdit and display it in the QLabel
entered_text = self.text_edit.text()
self.result_label.setText(f"Input Text: {entered_text}")
def main():
# Create a PyQt application
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
# Create an instance of the TextDisplayApp class
window = TextDisplayApp()
# Show the window
window.show()
# Run the application's event loop
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Explanation:
In the exercise above -
- Inport the necessary modules.
- Create a custom "TextDisplayApp" class that inherits from "QMainWindow".
- Inside the class, we create the window and widgets (QLineEdit, QPushButton, and QLabel) as well as set their properties and layout.
- Connect the button's click event to the display_text method, which retrieves the text from the 'QLineEdit' and displays it in the 'QLabel'.
- Create an instance of 'TextDisplayApp', show the window, and begin the application's event loop in the main function.
Output:
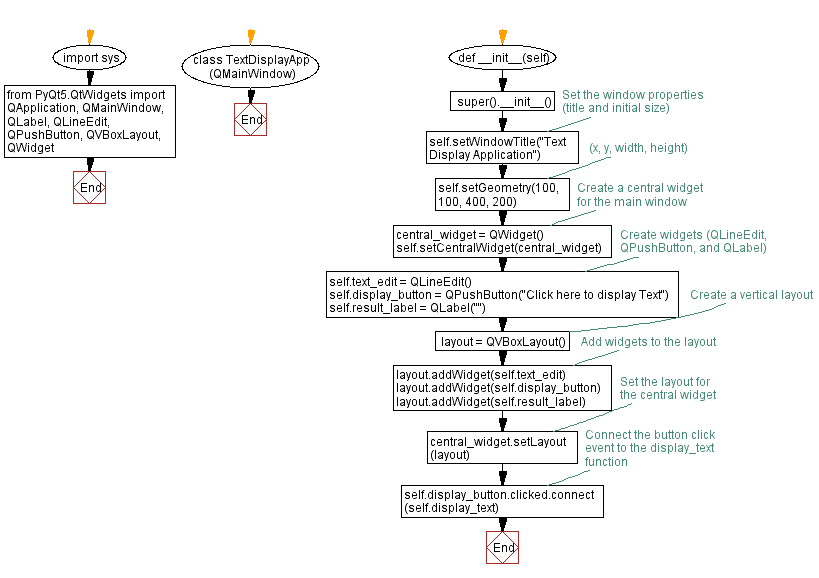
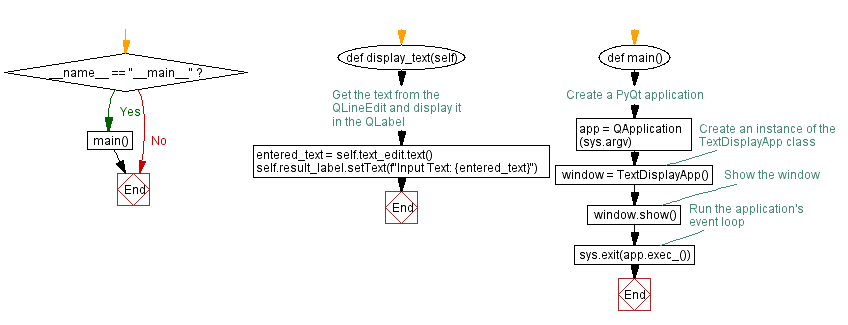
Flowchart:
Go to:
Previous: Python PyQt5 window with multiple widgets and layouts.
Next: Python PyQt text display application.
Python Code Editor:
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.