Python PyQt button actions example
Write a Python program that builds a PyQt application with two push buttons. Connect each button to a different slot function, and when clicked, have each button perform a unique action.
From doc.qt.io:
QApplication Class: The QApplication class manages the GUI application's control flow and main settings.
QWidget Class: The QWidget class is the base class of all user interface objects.
QPushButton Class: The QPushButton widget provides a command button.
QMessageBox Class: The QMessageBox class provides a modal dialog for informing the user or for asking the user a question and receiving an answer.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QPushButton, QMessageBox
# Slot function for the first button
def action_one(window):
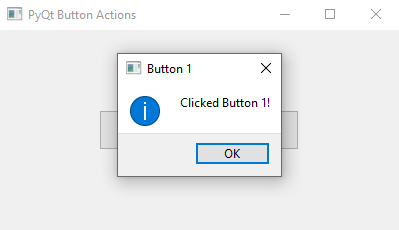
QMessageBox.information(window, "Button 1", "Clicked Button 1!")
# Slot function for the second button
def action_two(window):
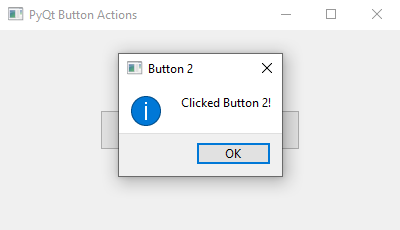
QMessageBox.information(window, "Button 2", "Clicked Button 2!")
def main():
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
# Create the main window
window = QWidget()
window.setWindowTitle("PyQt Button Actions")
window.setGeometry(100, 100, 400, 200) # (x, y, width, height)
# Create the first push button
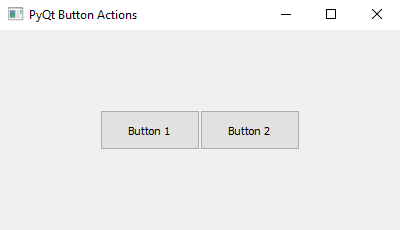
button1 = QPushButton("Button 1", window)
button1.setGeometry(100, 80, 100, 40) # (x, y, width, height)
# Create the second push button
button2 = QPushButton("Button 2", window)
button2.setGeometry(200, 80, 100, 40) # (x, y, width, height)
# Connect the first button's clicked signal to action_one slot
button1.clicked.connect(lambda: action_one(window))
# Connect the second button's clicked signal to action_two slot
button2.clicked.connect(lambda: action_two(window))
# Show the main window
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Explanation:
In the exercise above -
- Import the necessary modules from PyQt5.
- We define a custom "QWidget" class named "ButtonActions" that inherits from "QWidget". This class contains the entire GUI application logic.
- Inside the "ButtonActions" class, we create the main window and the two "QPushButton" widgets (button1 and button2).
- We connect the clicked signal of each button to its respective slot function using self.button1.clicked.connect(self.action_one) and self.button2.clicked.connect(self.action_two).
- The "action_one()" and "action_two()" slot functions display unique message boxes when called.
- In the main function, we create the PyQt application, instantiate the "ButtonActions" class, and show the main window.
Output:
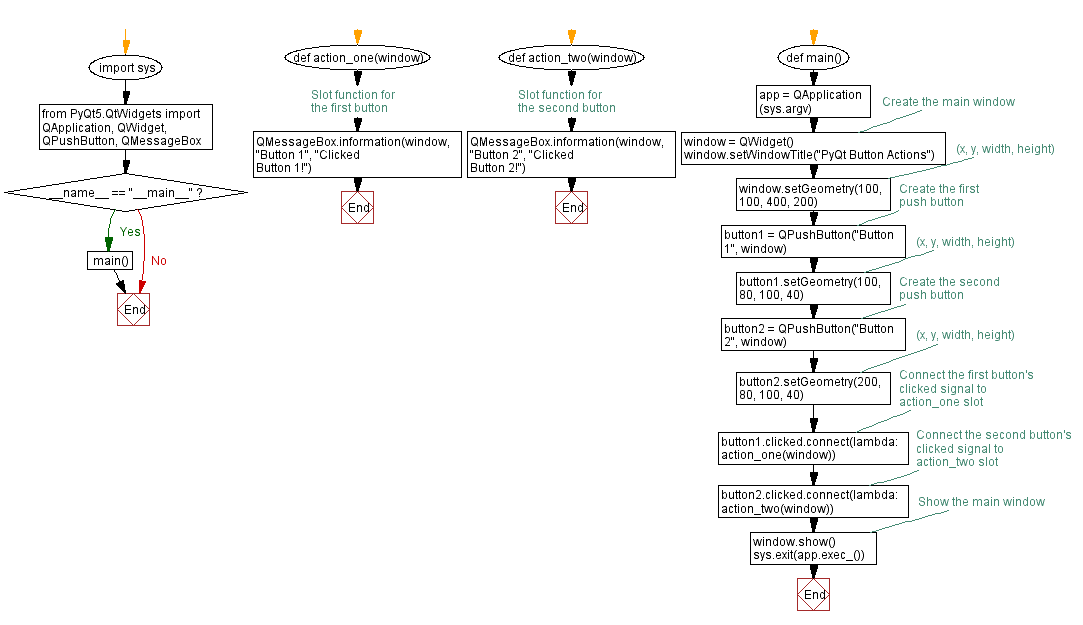
Flowchart:
Go to:
Previous: Python PyQt button click example.
Next: Python PyQt text updater application.
Python Code Editor:
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.