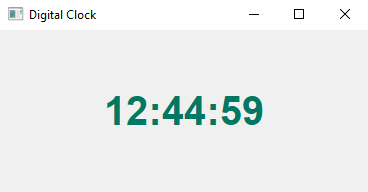
Python PyQt5 digital clock widget
Write a Python program to design a PyQt5 digital clock widget that updates the time every second.
From doc.qt.io:
QApplication Class: The QApplication class manages the GUI application's control flow and main settings.
QWidget Class: The QWidget class is the base class of all user interface objects.
QTimer Class: The QTimer class provides repetitive and single-shot timers.
QTime Class: The QTime class provides clock time functions.
QPainter Class: The QPainter class performs low-level painting on widgets and other paint devices.
QFont Class: The QFont class specifies a query for a font used for drawing text.
QColor Class: The QColor class provides colors based on RGB, HSV or CMYK values.
Qt module: PyQt5 is a set of Python bindings for the Qt application framework. It allows us to use Qt, a popular C++ framework, to create graphical user interfaces (GUIs) in Python.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget
from PyQt5.QtCore import QTimer, QTime
from PyQt5.QtGui import QPainter, QFont, QColor
from PyQt5.QtCore import Qt
class DigitalClock(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.setGeometry(100, 100, 300, 100)
self.setWindowTitle("Digital Clock")
self.timer = QTimer(self)
self.timer.timeout.connect(self.updateTime)
self.timer.start(1000) # Update every 1000 milliseconds (1 second)
self.current_time = QTime.currentTime()
def paintEvent(self, event):
painter = QPainter(self)
painter.setRenderHint(QPainter.Antialiasing)
# Configure font and color for the digital clock display
font = QFont('Arial', 30, QFont.Bold)
painter.setFont(font)
painter.setPen(QColor(0, 120, 100)) # Black color
# Format and display the current time
time_str = self.current_time.toString('hh:mm:ss')
painter.drawText(event.rect(), Qt.AlignCenter, time_str)
def updateTime(self):
# Update the current time and repaint the widget
self.current_time = QTime.currentTime()
self.repaint()
def main():
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
clock = DigitalClock()
clock.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Explanation:
In the exercise above -
- Import the necessary modules from PyQt5 for creating the application.
- Create a DigitalClock widget as a subclass of "QWidget".
- In the "initUI()" method, we set up the window's properties and create a QTimer to update the time every second.
- In the "paintEvent()" method, we use QPainter to draw the current time on the widget. We customize the digital clock font and color.
- The updateTime method is called by the timer's timeout signal. It retrieves the current time and triggers a repaint to update the displayed time.
- In the main function, we create an application instance, instantiate the DigitalClock, and start the application event loop.
Output:
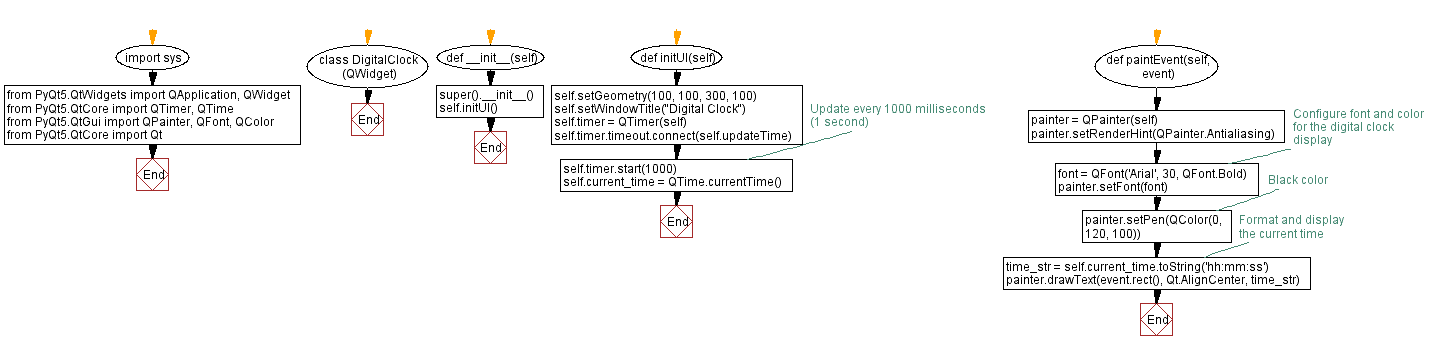
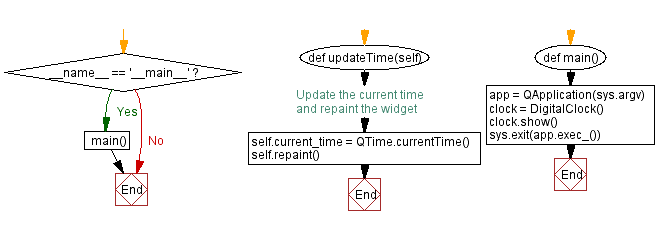
Flowchart:
Python Code Editor:
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.