Python: Create a Caesar encryption
Implement Caesar cipher encryption.
Write a Python program to create a Caesar encryption.
Note: In cryptography, a Caesar cipher, also known as Caesar's cipher, the shift cipher, Caesar's code or Caesar shift, is one of the simplest and most widely known encryption techniques. It is a type of substitution cipher in which each letter in the plaintext is replaced by a letter some fixed number of positions down the alphabet. For example, with a left shift of 3, D would be replaced by A, E would become B, and so on. The method is named after Julius Caesar, who used it in his private correspondence.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
#https://gist.github.com/nchitalov/2f2b03e5cf1e19da1525
# Define a function named caesar_encrypt that takes two arguments, 'realText' and 'step'.
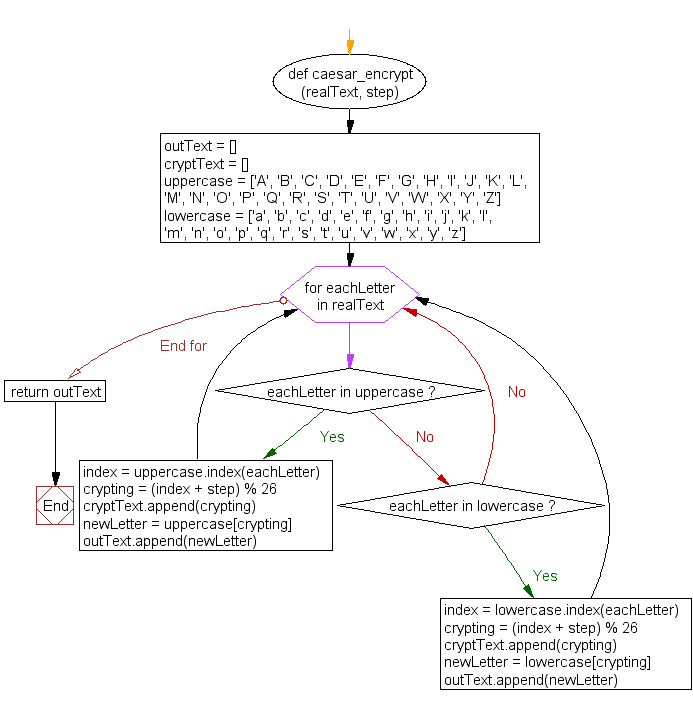
def caesar_encrypt(realText, step):
# Initialize two empty lists to store the output and the corresponding numeric values.
outText = []
cryptText = []
# Define lists for uppercase and lowercase letters of the English alphabet.
uppercase = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'M', 'N', 'O', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U', 'V', 'W', 'X', 'Y', 'Z']
lowercase = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z']
# Iterate through each letter in the 'realText' string.
for eachLetter in realText:
# Check if the letter is an uppercase letter.
if eachLetter in uppercase:
# Find the index of the letter in the 'uppercase' list.
index = uppercase.index(eachLetter)
# Perform Caesar cipher encryption by adding 'step' and taking the modulus 26.
crypting = (index + step) % 26
cryptText.append(crypting)
# Find the new letter corresponding to the encrypted value and append it to the 'outText' list.
newLetter = uppercase[crypting]
outText.append(newLetter)
# Check if the letter is a lowercase letter.
elif eachLetter in lowercase:
# Find the index of the letter in the 'lowercase' list.
index = lowercase.index(eachLetter)
# Perform Caesar cipher encryption by adding 'step' and taking the modulus 26.
crypting = (index + step) % 26
cryptText.append(crypting)
# Find the new letter corresponding to the encrypted value and append it to the 'outText' list.
newLetter = lowercase[crypting]
outText.append(newLetter)
# Return the 'outText' list containing the encrypted letters.
return outText
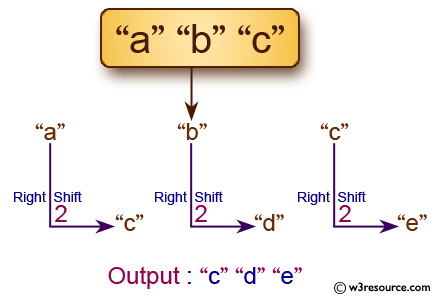
# Call the caesar_encrypt function with the input 'abc' and a step of 2, and store the result in 'code'.
code = caesar_encrypt('abc', 2)
# Print an empty line for spacing.
print()
# Print the 'code', which contains the result of the Caesar cipher encryption.
print(code)
# Print an empty line for spacing.
print()
Sample Output:
['c', 'd', 'e']
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Python program to encrypt a message using a Caesar cipher with a fixed shift value, preserving letter case.
- Write a Python program to implement both encryption and decryption functions for a Caesar cipher.
- Write a Python program to create a Caesar cipher that rotates letters while leaving non-alphabetic characters unchanged.
- Write a Python program to allow dynamic input of shift values and perform Caesar cipher encryption on the input text.
Go to:
Previous: Write a Python program to check whether a string starts with specified characters.
Next: Write a Python program to display formatted text (width=50) as output.
Python Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
