Python Multi-threading and Concurrency: Multi-threaded merge sort implementation
5. Multi-threaded Merge Sort
Write a Python program to implement a multi-threaded merge sort algorithm.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
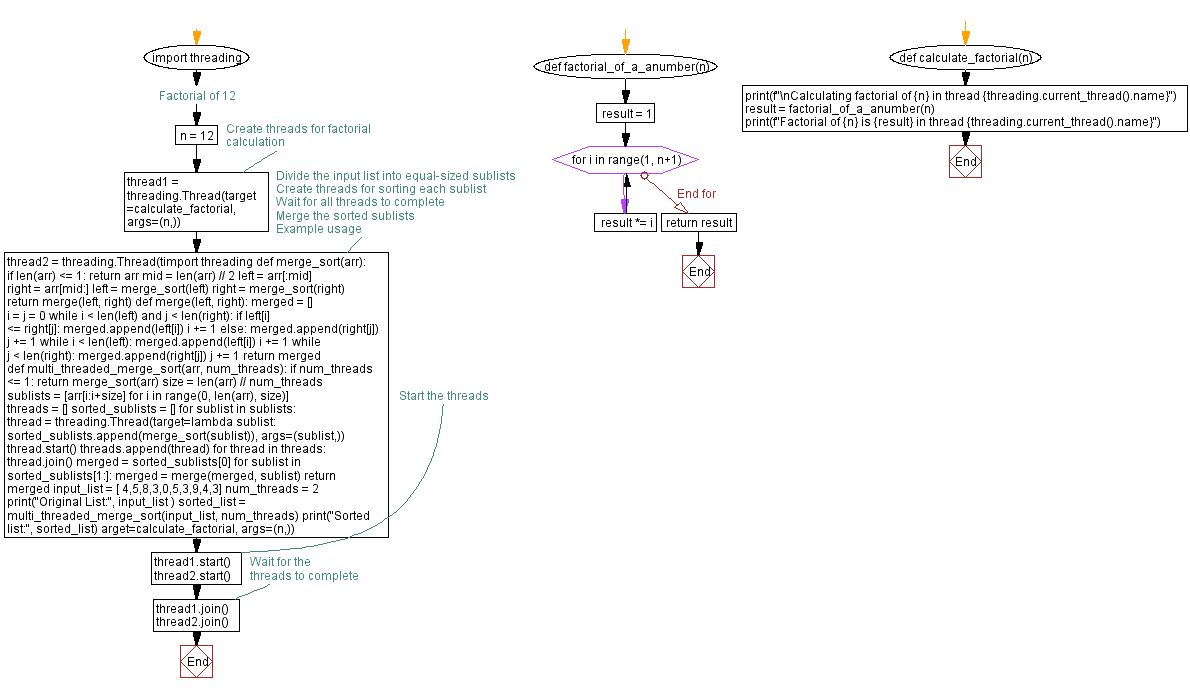
import threading
def merge_sort(arr):
if len(arr) <= 1:
return arr
mid = len(arr) // 2
left = arr[:mid]
right = arr[mid:]
left = merge_sort(left)
right = merge_sort(right)
return merge(left, right)
def merge(left, right):
merged = []
i = j = 0
while i < len(left) and j < len(right):
if left[i] <= right[j]:
merged.append(left[i])
i += 1
else:
merged.append(right[j])
j += 1
while i < len(left):
merged.append(left[i])
i += 1
while j < len(right):
merged.append(right[j])
j += 1
return merged
def multi_threaded_merge_sort(arr, num_threads):
if num_threads <= 1:
return merge_sort(arr)
# Divide the input list into equal-sized sublists
size = len(arr) // num_threads
sublists = [arr[i:i+size] for i in range(0, len(arr), size)]
# Create threads for sorting each sublist
threads = []
sorted_sublists = []
for sublist in sublists:
thread = threading.Thread(target=lambda sublist: sorted_sublists.append(merge_sort(sublist)), args=(sublist,))
thread.start()
threads.append(thread)
# Wait for all threads to complete
for thread in threads:
thread.join()
# Merge the sorted sublists
merged = sorted_sublists[0]
for sublist in sorted_sublists[1:]:
merged = merge(merged, sublist)
return merged
# Example usage
input_list = [ 4,5,8,3,0,5,3,9,4,3]
num_threads = 2
print("Original List:", input_list )
sorted_list = multi_threaded_merge_sort(input_list, num_threads)
print("Sorted list:", sorted_list)
Sample Output:
Original List: [4, 5, 8, 3, 0, 5, 3, 9, 4, 3] Sorted list: [0, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 5, 8, 9]
Explanation:
In the above exercise, we define a "merge_sort()" function that implements the regular merge sort algorithm to sort a given list. A "merge()" function is also defined, which merges two sorted lists into one.
The "multi_threaded_merge_sort()" function takes the input list and the number of threads as arguments. It divides the input list into equal-sized sublists and creates threads for sorting each sublist. Each thread runs the "merge_sort()" function independently. After all the threads complete, the program merges the sorted sublists using the "merge()" function.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Python program to implement merge sort using threads by sorting two halves of the list concurrently and then merging the sorted halves.
- Write a Python script to divide a list into segments, sort each segment in a separate thread using merge sort, and then merge the sorted segments.
- Write a Python function that performs multi-threaded merge sort and prints the sorted subarrays at each merge step.
- Write a Python program to benchmark multi-threaded merge sort against the built-in sorted() function using different list sizes.
Go to:
Previous: Multi-threaded factorial calculation.
Next: Multi-threaded quicksort implementation.
Python Code Editor :
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
