Python Multi-threading and concurrency: Concurrent HTTP requests with threads
7. Concurrent HTTP Requests
Write a Python program that performs concurrent HTTP requests using threads.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
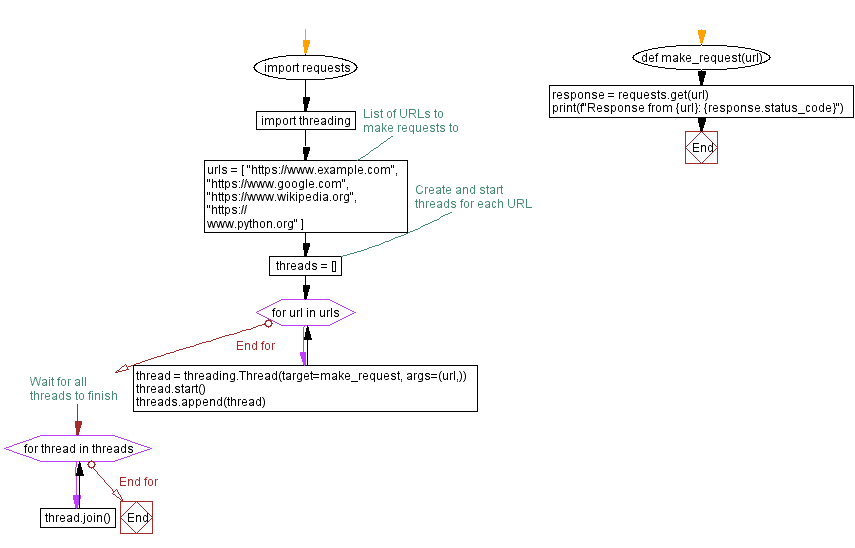
import requests
import threading
def make_request(url):
response = requests.get(url)
print(f"Response from {url}: {response.status_code}")
# List of URLs to make requests to
urls = [
"https://www.example.com",
"https://www.google.com",
"https://www.wikipedia.org",
"https://www.python.org"
]
# Create and start threads for each URL
threads = []
for url in urls:
thread = threading.Thread(target=make_request, args=(url,))
thread.start()
threads.append(thread)
# Wait for all threads to finish
for thread in threads:
thread.join()
Sample Output:
Response from https://www.google.com: 200 Response from https://www.wikipedia.org: 200 Response from https://www.python.org: 200 Response from https://www.example.com: 200
Explanation:
In the above exercise,
- The "make_request()" function sends an HTTP GET request to a given URL using the requests library. The function prints the URL and the response status code.
- The program creates a list of URLs you want to request. It then iterates over the URLs, creates a thread for each URL using threading.Thread, and starts the thread by calling its start method. The threads are stored in a list for later joining.
- After starting all the threads, the program uses a loop to join each thread using the join method. This ensures that the program waits for all threads to finish before proceeding.
- Finally, the program prints a message indicating that all requests have been fulfilled.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Python program to perform concurrent HTTP GET requests using threads and then print the status code of each response.
- Write a Python script to create multiple threads that make HTTP requests to different URLs concurrently and log the response times.
- Write a Python function to use threading for concurrent HTTP requests, then aggregate and display the results in a summary report.
- Write a Python program to simulate concurrent HTTP requests using threads, handle exceptions for failed requests, and print a detailed log for each request.
Go to:
Previous: Multi-threaded quicksort implementation.
Next: Python Asynchronous Exercises Homr.
Python Code Editor :
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
