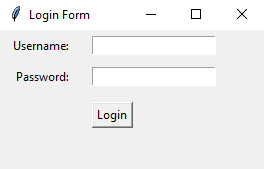
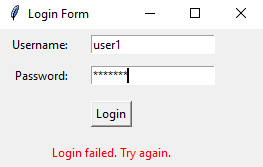
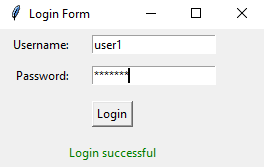
Create a Python login form with Tkinter's grid manager
Write a Python program that designs a simple login form with labels and Entry widgets, arranging them in a grid using the Grid geometry manager.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
import tkinter as tk
# Create a function to handle the login button click event
def login():
username = username_entry.get()
password = password_entry.get()
if username == "user1" and password == "abcd123":
login_status.config(text="Login successful", fg="green")
else:
login_status.config(text="Login failed. Try again.", fg="red")
# Create the main Tkinter window
parent = tk.Tk()
parent.title("Login Form")
# Create labels and Entry widgets for username and password
username_label = tk.Label(parent, text="Username:")
password_label = tk.Label(parent, text="Password:")
username_entry = tk.Entry(parent)
password_entry = tk.Entry(parent, show="*") # Show '*' for password entry
# Create a Login button
login_button = tk.Button(parent, text="Login", command=login)
# Create a label to display login status
login_status = tk.Label(parent, text="", fg="black")
# Use the Grid geometry manager to arrange widgets
username_label.grid(row=0, column=0, padx=10, pady=5, sticky="E")
username_entry.grid(row=0, column=1, padx=10, pady=5)
password_label.grid(row=1, column=0, padx=10, pady=5, sticky="E")
password_entry.grid(row=1, column=1, padx=10, pady=5)
login_button.grid(row=2, column=0, columnspan=2, padx=10, pady=10)
login_status.grid(row=3, column=0, columnspan=2, padx=10, pady=5)
# Run the Tkinter main loop
parent.mainloop()
Explanation:
In the exercise above -
- Import the tkinter module as 'tk'.
- Create the main Tkinter window using tk.Tk() and set its title to "Login Form."
- Labels (username_label and password_label) and entry widgets (username_entry and password_entry) should be created for username and password input. The show="*" option hides the actual characters in the password entry.
- Create a Login button (login_button) and a label (login_status) to display the login status.
- For grid layouts, we use the "grid()" method. Each widget has a row and column position specified. "columnspan" is used to make login_button and login_status span across two columns.
- Define a login() function to handle the login button click event. For demonstration purposes, it compares the entered username and password with "user1" and "abcd123". The login status is updated accordingly.
- Finally the Tkinter main loop is started by root.mainloop(), which displays the login form in a grid layout and keeps the GUI application running.
Sample Output:
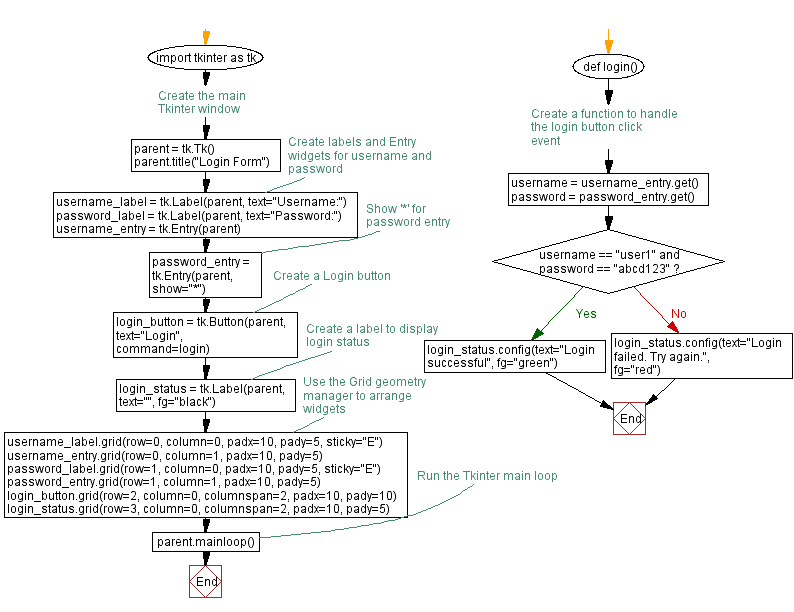
Flowchart:
Go to:
Previous: Organize widgets with Python Tkinter's grid manager.
Next: Build a Python calculator interface with Tkinter's grid manager.
Python Code Editor:
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.