Implementing Retry Mechanism in Python urllib3 for Resilient HTTP Requests
Write a Python program that sets up a retry mechanism for failed requests with urllib3.Retry class.
Sample Solution:
Python Code :
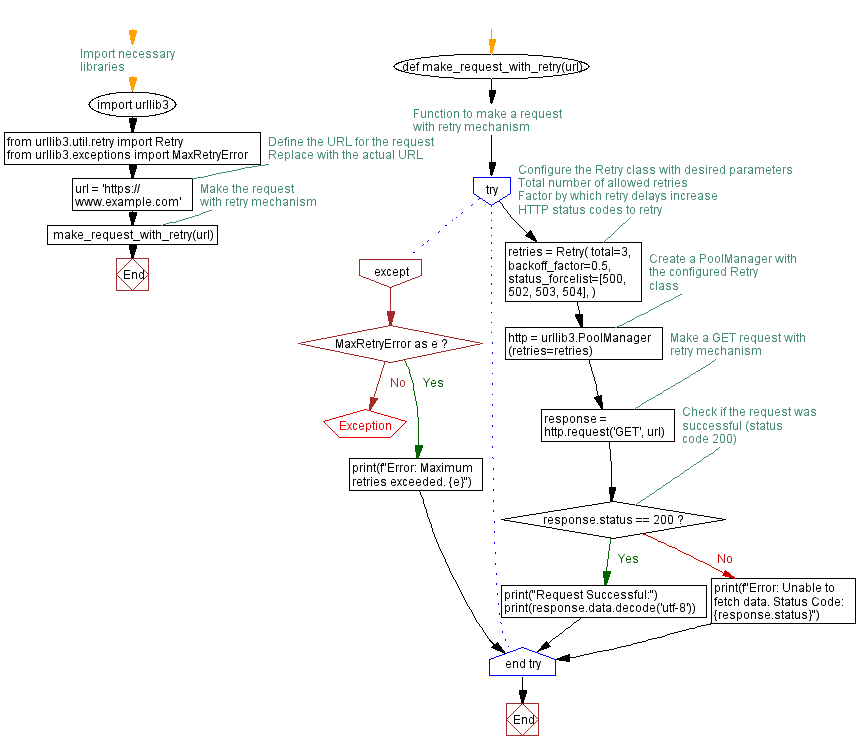
# Import necessary libraries
import urllib3
from urllib3.util.retry import Retry
from urllib3.exceptions import MaxRetryError
# Function to make a request with retry mechanism
def make_request_with_retry(url):
try:
# Configure the Retry class with desired parameters
retries = Retry(
total=3, # Total number of allowed retries
backoff_factor=0.5, # Factor by which retry delays increase
status_forcelist=[500, 502, 503, 504], # HTTP status codes to retry
)
# Create a PoolManager with the configured Retry class
http = urllib3.PoolManager(retries=retries)
# Make a GET request with retry mechanism
response = http.request('GET', url)
# Check if the request was successful (status code 200)
if response.status == 200:
print("Request Successful:")
print(response.data.decode('utf-8'))
else:
print(f"Error: Unable to fetch data. Status Code: {response.status}")
except MaxRetryError as e:
print(f"Error: Maximum retries exceeded. {e}")
# Define the URL for the request
url = 'https://www.example.com' # Replace with the actual URL
# Make the request with retry mechanism
make_request_with_retry(url)
Sample Output:
Request Successful:
<!doctype html<
<html<
<head<
<title<Example Domain</title<
<meta charset="utf-8" /<
<meta http-equiv="Content-type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" /<
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" /<
<style type="text/css"<
body {
background-color: #f0f0f2;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
font-family: -apple-system, system-ui, BlinkMacSystemFont, "Segoe UI", "Open Sans", "Helvetica Neue", Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
}
div {
width: 600px;
margin: 5em auto;
padding: 2em;
background-color: #fdfdff;
border-radius: 0.5em;
box-shadow: 2px 3px 7px 2px rgba(0,0,0,0.02);
}
a:link, a:visited {
color: #38488f;
text-decoration: none;
}
@media (max-width: 700px) {
div {
margin: 0 auto;
width: auto;
}
}
</style<
</head<
<body<
<div<
<h1<Example Domain</h1<
<p<This domain is for use in illustrative examples in documents. You may use this
domain in literature without prior coordination or asking for permission.</p<
<p<<a href="https://www.iana.org/domains/example"<More information...</a<</p<
</div<
</body<
</html<
runfile('C:/Users/ME/untitled30.py', wdir='C:/Users/ME')
Request Successful:
<!doctype html<
<html<
<head<
<title<Example Domain</title<
<meta charset="utf-8" /<
<meta http-equiv="Content-type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" /<
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" /<
<style type="text/css"<
body {
background-color: #f0f0f2;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
font-family: -apple-system, system-ui, BlinkMacSystemFont, "Segoe UI", "Open Sans", "Helvetica Neue", Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
}
div {
width: 600px;
margin: 5em auto;
padding: 2em;
background-color: #fdfdff;
border-radius: 0.5em;
box-shadow: 2px 3px 7px 2px rgba(0,0,0,0.02);
}
a:link, a:visited {
color: #38488f;
text-decoration: none;
}
@media (max-width: 700px) {
div {
margin: 0 auto;
width: auto;
}
}
</style<
</head<
<body<
<div<
<h1<Example Domain</h1<
<p<This domain is for use in illustrative examples in documents. You may use this
domain in literature without prior coordination or asking for permission.</p<
<p<<a href="https://www.iana.org/domains/example"<More information...</a<</p<
</div<
</body<
</html<
Explanation:
Here's a brief explanation of the above Python urllib3 library code:
- Import Libraries: Import the necessary libraries, including "urllib3" for making HTTP requests.
- Define Function: Create a function "make_request_with_retry()" that takes a URL as a parameter and makes a request with a retry mechanism.
- Configure Retry Class: Create a "Retry" class instance with parameters like 'total' (total number of retries), 'backoff_factor' (factor by which retry delays increase), and 'status_forcelist' (HTTP status codes to retry).
- Create PoolManager: Create an instance of "urllib3.PoolManager" with the configured 'Retry' class.
- Make Request with Retry: Use the "http.request" method to make a GET request with the retry mechanism.
- Handle Response: Check if the request was successful (status code 200) and print the response. Otherwise, print an error message.
- Exception Handling: Catch and handle 'MaxRetryError' exceptions that might occur when the maximum number of retries is exceeded.
- Make Request with Retry: Call the "make_request_with_retry()" function to initiate the request with the configured retry mechanism.
Flowchart:
Python Code Editor :
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
Previous: Implementing a Custom SSL Context for Secure HTTPS requests in Python urllib3.
Next: Python file upload with urllib3: Making POST Requests simplified.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
