Python Program: Maximum connection Pool size analysis
Write a Python program that sets the maximum connection pool size and observe how it affects the number of simultaneous connections made. Use urllib3.
Sample Solution:
Python Code :
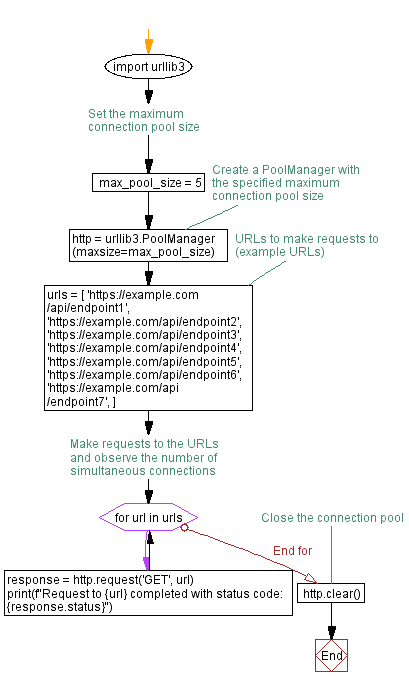
import urllib3
# Set the maximum connection pool size
max_pool_size = 5
# Create a PoolManager with the specified maximum connection pool size
http = urllib3.PoolManager(maxsize=max_pool_size)
# URLs to make requests to (example URLs)
urls = [
'https://example.com/api/endpoint1',
'https://example.com/api/endpoint2',
'https://example.com/api/endpoint3',
'https://example.com/api/endpoint4',
'https://example.com/api/endpoint5',
'https://example.com/api/endpoint6',
'https://example.com/api/endpoint7',
]
# Make requests to the URLs and observe the number of simultaneous connections
for url in urls:
response = http.request('GET', url)
print(f"Request to {url} completed with status code: {response.status}")
# Close the connection pool
http.clear()
Sample Output:
Request to https://example.com/api/endpoint1 completed with status code: 404 Request to https://example.com/api/endpoint2 completed with status code: 404 Request to https://example.com/api/endpoint3 completed with status code: 404 Request to https://example.com/api/endpoint4 completed with status code: 404 Request to https://example.com/api/endpoint5 completed with status code: 404 Request to https://example.com/api/endpoint6 completed with status code: 404 Request to https://example.com/api/endpoint7 completed with status code: 404
Explanation:
Here's a brief explanation of the above Python urllib3 library code:
- Setting Maximum Connection Pool Size: The max_pool_size variable specifies the maximum size of the connection pool.
- Creating PoolManager: A PoolManager object is created using urllib3.PoolManager(maxsize=max_pool_size) with the specified maximum connection pool size.
- Defining URLs: A list of example URLs ('urls') is defined to simulate requests to different endpoints.
- Making Requests: A loop iterates through the URLs, and for each URL, a GET request is made using http.request('GET', url).
- Observing Connections: The status code of each request is printed to observe how many connections are made simultaneously based on the maximum pool size.
- Closing Connection Pool: Finally, the connection pool is cleared using "http.clear()" to release any resources associated with it.
Flowchart:
Python Code Editor :
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
Previous: Python File Upload: Simulate POST request with multipart/Form-Data.
Next: Python Program: Observing urllib3 Response compression handling.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
