Python: bytearray() function
bytearray() function
The bytearray() function is used to get a bytearray object.
Syntax:
bytearray([source[, encoding[, errors]]])
Version:
(Python 3)
The optional source parameter can be used to initialize the array in a few different ways:
- If it is a string, you must also give the encoding (and optionally, errors) parameters; bytearray() then converts the string to bytes using str.encode().
- If it is an integer, the array will have that size and will be initialized with null bytes.
- If it is an object conforming to the buffer interface, a read-only buffer of the object will be used to initialize the bytes array.
- If it is an iterable, it must be an iterable of integers in the range 0 <= x < 256, which are used as the initial contents of the array.
Without an argument, an array of size 0 is created.
Return value
Return a new array of bytes.
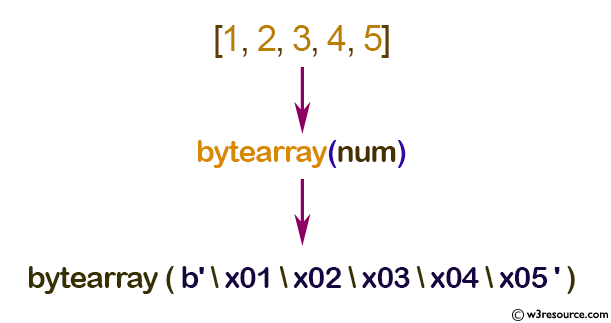
Example: Array of bytes from an iterable list
num = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
a = bytearray(num)
print(a)
Output:
bytearray(b'\x01\x02\x03\x04\x05')
Pictorial Presentation:
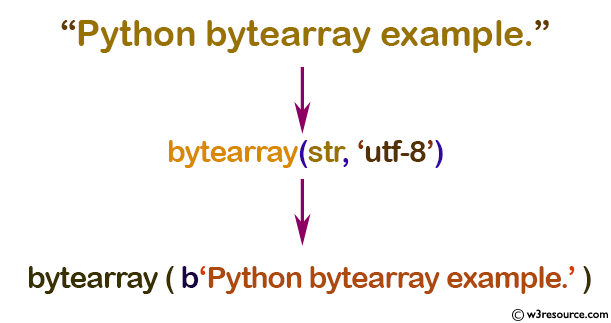
Example: Array of bytes from a string
str = "Python bytearray example."
# string with encoding 'utf-8'
a = bytearray(str, 'utf-8')
print(a)
Output:
bytearray(b'Python bytearray example.')
Pictorial Presentation:
Example: Array of bytes of given integer size:
size = 10
a = bytearray(size)
print(a)
Output:
bytearray(b'\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00')
Python Code Editor:
Previous: bool()
Next: bytes()
Test your Python skills with w3resource's quiz
