Python: bytes() function
bytes() function
The bytes() function is used to get a new 'bytes' object.
Note: bytes is an immutable version of bytearray – it has the same non-mutating methods and the same indexing and slicing behavior.
Accordingly, constructor arguments are interpreted as for bytearray()
Syntax:
bytes([source[, encoding[, errors]]])
Version:
(Python 3.2.5)
Return value:
Return a new 'bytes' object, which is an immutable sequence of integers in the range 0 <= x < 256.
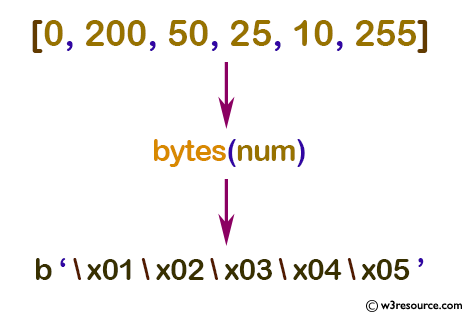
Example: Convert iterable list to bytes
num = [0, 200, 50, 25, 10, 255]
a = bytes(num)
print(a)
Output:
b'\x01\x02\x03\x04\x05'
Pictorial Presentation:
Example: Create a byte of given integer size
s = 10
a = bytes(s)
print(a)
Output:
b'\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00'
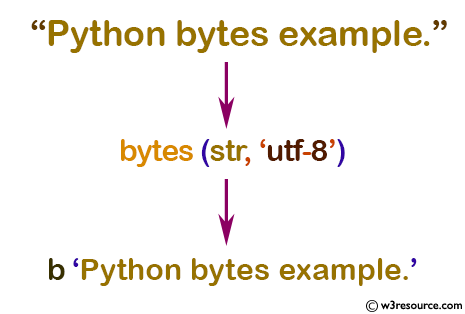
Example: Convert string to bytes
str = "Python bytes example."
# string with encoding 'utf-8'
a = bytes(str, 'utf-8')
print(a)
Output:
b'Python bytes example.'
Pictorial Presentation:
Python Code Editor:
Previous: bytearray()
Next: callable()
Test your Python skills with w3resource's quiz
