Python: round() function
round() function
The round() function returns the rounded floating point value number, rounded to ndigits digits after the decimal point. If ndigits is omitted, it defaults to zero.
Note: For the built-in types supporting round(), values are rounded to the closest multiple of 10 to the power minus ndigits; if two multiples are equally close, rounding is done toward the even choice (so, for example, both round(0.5) and round(-0.5) are 0, and round(1.5) is 2). The return value is an integer if called with one argument, otherwise of the same type as number.
Version:
(Python 3.2.5)
Syntax:
round(number[, ndigits])
Parameter:
| Name | Description | Required / Optional |
|---|---|---|
| number | Number to be rounded. | Required |
| ndigits | The number of decimals to use. Default is 0 | Optional |
Return value:
Floating point value number.
Example-1: Python round() function
# for integers
print(round(5))
# for floating point
print(round(15.7))
# even choice
print(round(7.3))
Output:
5 16 7
Pictorial Presentation:
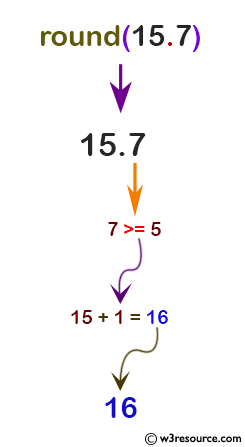
Pictorial Presentation:

Example-2: Python round() function
print(round(5.7754, 2))
# cannot be represented exactly as float
print(round(5.6758, 3))
Output:
5.78 5.676
Python Code Editor:
Previous: reversed()
Next: set()
Test your Python skills with w3resource's quiz
