Python: float() function
float() function
The float() function is used to convert the specified value into a floating point number.
Note: If the argument is a string, it should contain a decimal number, optionally preceded by a sign, and optionally embedded in whitespace. The optional sign may be '+' or '-'; a '+' sign has no effect on the value produced. The argument may also be a string representing a NaN (not-a-number), or a positive or negative infinity. The following grammar after leading and trailing whitespace characters are removed:
sign ::= "+" | "-" infinity ::= "Infinity" | "inf" nan ::= "nan" numeric_value ::= floatnumber | infinity | nan numeric_string ::= [sign] numeric_value
Return value :
If no argument is given, 0.0 is returned.
Version
(Python 3.2.5)
Syntax:
float([x])
Return value:
Floating point number, if no argument is given, 0.0 is returned.
Example: Python float() function
# for floats
print(float(2.25))
# for string floats with whitespaces
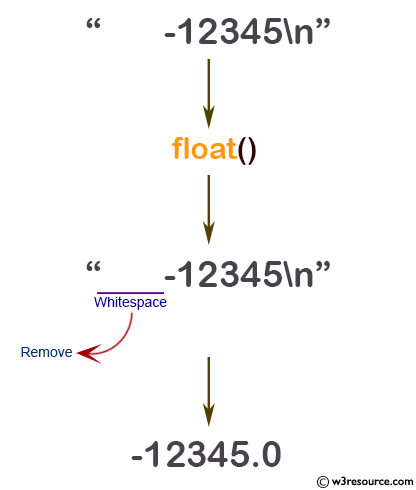
print(float(" -12345\n"))
# for string floats
print(float("-15.55"))
print(float("1e-005"))
print(float("+1E7"))
print(float("-Infinity"))
Output:
2.25 -12345.0 -15.55 1e-05 10000000.0 -inf
Pictorial Presentation:
The float type is described in Numeric Types — int, float, complex.
Python Code Editor:
Previous: filter()
Next: format()
Test your Python skills with w3resource's quiz
