Python: hex() function
hex() function
The hex() function converts an integer number to a lowercase hexadecimal string prefixed with "0x". Hexadecimal is a base-16 number system, commonly used in programming to represent binary data more compactly.
Version:
Available in: Python 3.2.5 and later
Syntax:
hex(x)
Parameter:
| Name | Description | Required / Optional |
|---|---|---|
| x | An integer number to convert to hexadecimal | Required |
Return Value:
The function returns the hexadecimal representation of an integer as a string, prefixed with "0x".
Example: Using hex() with integers
number = 127
print(number, 'in hex =', hex(number))
number = 0
print(number, 'in hex =', hex(number))
number = -35
print(number, 'in hex =', hex(number))
returnType = type(hex(number))
print('Return type from hex() is', returnType)
Output:
127 in hex = 0x7f 0 in hex = 0x0 -35 in hex = -0x23 Return type from hex() is <class 'str'>
Explanation:
- 127 is represented as 0x7f in hexadecimal.
- 0 becomes 0x0, and negative integers also retain the 0x prefix with the negative sign (-0x23 for -35).
- The return type of the hex() function is <class 'str'>, indicating that it returns a string.
Example: Using hex() with floating-point numbers
While the hex() function is used for integers, Python provides a similar method for floating-point numbers using the float.hex() method, which converts floating-point numbers to a hexadecimal floating-point string.
number = 5.25
print(number, 'in hex =', float.hex(number))
number = 0.0
print(number, 'in hex =', float.hex(number))
number = 15.5
print(number, 'in hex =', float.hex(number))
Output:
5.25 in hex = 0x1.5000000000000p+2 0.0 in hex = 0x0.0p+0 15.5 in hex = 0x1.f000000000000p+3
Explanation:
- The float.hex() method represents a floating-point number in a hexadecimal format.
- For 5.25, it converts to 0x1.5000000000000p+2, where p represents the power of 2 (binary exponent).
- 15.5 is represented as 0x1.f000000000000p+3, and 0.0 as 0x0.0p+0.
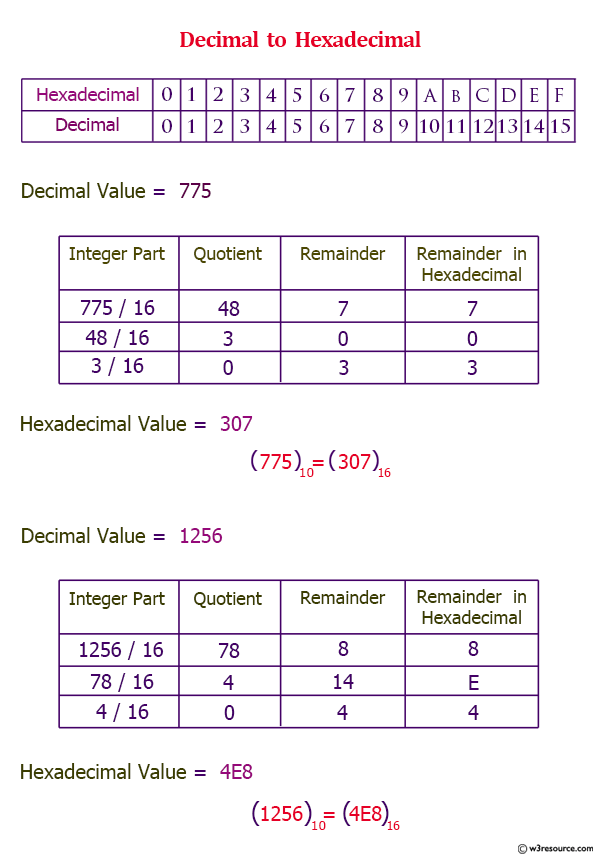
Pictorial Presentation:
Summary:
- The hex() function is useful for converting integers to hexadecimal strings, especially when working with low-level data.
- For floating-point numbers, Python provides the float.hex() method, which converts floats to a hexadecimal representation.
Python Code Editor:
Test your Python skills with w3resource's quiz
