Python: pow() function
pow() function
The pow() function is used to get the value of x to the power of y (xy). If z is present, return x to the power y, modulo z (computed more efficiently than pow(x, y) % z).
Version:
(Python 3.2.5)
Syntax:
pow(x, y[, z])
Parameter:
| Name | Description | Required / Optional |
|---|---|---|
| x | A number (the base) which is to be powered. | Required |
| y | A number (the exponent) which is to be powered with x. | Required |
| z | A number which is to be used for modulus operation. | Optional |
Example: Python pow() function
# positive a, positive b (a**b)
print(pow(4, 4))
# negative a, positive b
print(pow(-4, 4))
# positive a, negative b (a**-b)
print(pow(4, -4))
# negative a, negative b
print(pow(-4, -4))
Output:
256 256 0.00390625 0.00390625
Pictorial Presentation:
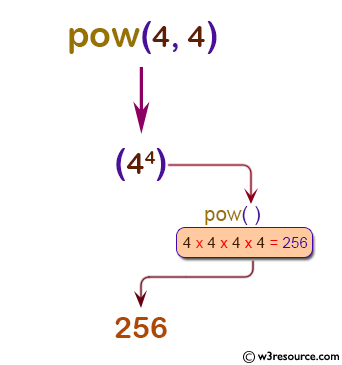
Example: Python pow() with three arguments (x**y) % z
a = 3
b = 5
c = 7
print(pow(a, b, c))
Output:
5
Python Code Editor:
Test your Python skills with w3resource's quiz
